Bailey Bridge Maintenance: The Art of Ensuring Safety and Prolonging Lifespan
In the vast expanse of bridge engineering, the Bailey Bridge stands out with its unique brilliance, illuminating countless paths of traversal and challenge. From its military origins during World War II, to its widespread application in various complex environments today, the Bailey Bridge has not only witnessed historical transitions but also emerged as a vital bridge type that connects both banks and fosters development. However, like any sophisticated mechanical structure, the Bailey Bridge's long-term stable operation relies on scientific and effective maintenance. This article delves into the significance of Bailey Bridge maintenance, routine maintenance content, regular inspections and repairs, as well as future maintenance trends, to explore how to safeguard the bridge's safety and prolong its lifespan.
I. The Significance of Maintenance: The Cornerstone of Safety and Development
As a critical transportation infrastructure, the safe and stable operation of the Bailey Bridge is directly linked to the safety of people's lives and property, as well as regional economic development. Maintenance not only promptly identifies and eliminates potential safety hazards, preventing traffic accidents caused by bridge damage, but also effectively extends the bridge's service life, mitigating economic burdens associated with frequent repairs or replacements. Thus, conducting scientific and reasonable maintenance for the Bailey Bridge serves as the cornerstone of ensuring its safety and development.
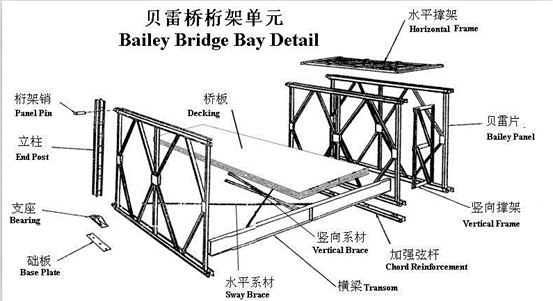
II. Routine Maintenance Content: Meticulous Care and Attention
Routine maintenance forms the foundation of Bailey Bridge preservation efforts, requiring management and maintenance personnel to possess a high degree of responsibility and professional expertise. Specifically, routine maintenance encompasses the following aspects:
Cleaning and Preservation: Regularly clearing debris, dust, and standing water from the bridge deck and ancillary facilities to maintain a clean appearance and prevent corrosion that could compromise structural safety.
EVERCROSS -GREAT WALL STEEL BRIDGE SPECIFICATION | |
EVERCROSS -GREAT WALL | Bailey bridge (Compact-200, Compact-100, LSB, PB100, China-321, BSB) |
DESIGN SPANS | 10M TO 300M Single span |
CARRIAGE WAY | SINGLE LANE, DOUBLE LANES, MULTILANE, WALKWAY, ETC |
LOADING CAPACITY | AASHTO HL93.HS15-44, HS20-44, HS25-44, |
STEEL GRADE | EN10025 S355JR S355J0/EN10219 S460J0/EN10113 S460N/BS4360 Grade 55C |
CERTIFICATES | ISO9001, ISO14001, ISO45001, EN1090, CIDB, COC, PVOC, SONCAP, etc. |
WELDING | AWS D1.1/AWS D1.5 |
BOLTS | ISO898, AS/NZS1252, BS3692 or equivalent |
GALVANIZATION CODE | ISO1461,AS/NZS 4680,ASTM-A123,BS1706,or equivalent |
Connecting Components Inspection: Inspecting the tightness and integrity of all bridge connections, promptly replacing damaged ones to ensure the overall stability of the bridge structure.
Deck Condition Monitoring: Routinely assessing the evenness of the deck pavement, identifying cracks or depressions, and promptly repairing damaged areas to prevent vehicle bumpiness or further structural damage.
Drainage System Maintenance: Ensuring the drainage system remains unobstructed to prevent water accumulation that could erode the bridge foundation.
III. Regular Inspections and Repairs: Preventing Issues Before They Arise
In addition to routine maintenance, the Bailey Bridge necessitates periodic professional inspections and repairs. These tasks are typically undertaken by specialized bridge inspection teams, utilizing advanced detection technologies and equipment to conduct comprehensive and meticulous assessments.
Structural Inspection: Employing non-destructive testing techniques to scan and examine the bridge structure, uncovering potential cracks, deformations, or corrosion issues, providing a scientific basis for repair work.
Load-Bearing Capacity Evaluation: Assessing the bridge's actual load-bearing capacity against design requirements, implementing reinforcement measures as necessary.
Repair and Reinforcement: Developing detailed repair plans based on inspection findings, utilizing suitable materials and techniques to restore the bridge's original load-bearing capacity and safety performance.

IV. Future Maintenance Trends: Embracing Intelligence and Green Initiatives
With technological advancements and heightened environmental awareness, the maintenance of Bailey Bridges will embrace new trends.
Intelligent Maintenance: Harnessing the power of IoT, big data, and AI to achieve real-time monitoring and early warning of bridge health conditions, enhancing maintenance efficiency and accuracy. By leveraging smart analysis systems, potential issues can be anticipated, allowing for proactive maintenance planning that minimizes disruptions to traffic.
Green Maintenance: Prioritizing environmental protection and sustainable development during maintenance activities, employing eco-friendly materials and techniques for repairs and reinforcements. Additionally, reinforcing efforts to protect and restore the bridge's surrounding ecosystem, fostering a harmonious coexistence between the bridge and nature.
In conclusion, the maintenance of Bailey Bridges is a complex yet meticulous endeavor, necessitating the dedication and professional expertise of both management and maintenance personnel. Through scientific and reasonable maintenance measures, we can ensure the safe and stable operation of Bailey Bridges, extending their lifespans, and thereby contributing significantly to human transportation endeavors and societal development. As technology continues to advance and environmental consciousness grows, we can anticipate the maintenance of Bailey Bridges becoming increasingly intelligent and eco-friendly, fostering the creation of safer, more convenient, and greener transportation networks.







 Certified
Certified